Over the last month we have written several pieces of content reviewing the differences in the infrastructure, software, and categories of file sharing/file transfer solutions. This blog will be the last installment of this series. In this blog we deep dive into some of the largest security breaches in the file transfer/file sharing industry, the consequences and how to avoid falling victim to a cybersecurity attack.
One of the largest growing security threats in business today is data and information security. Protecting your organizations files and other important data from hackers is crucial to business operations. Unfortunately, the damaging effects of a data breach have impacted some of the largest companies in the world like Accellion, AWS, Morgan Stanley, CVS, Wegmans, Microsoft, Facebook, HubSpot and more. On the surface, many of these organizations seemed like they would be impenetrable.
The size or nature of your business does not matter. It is more important than ever to protect your information from hackers – specifically enterprise data such as personal identifiable information (PII), personal healthcare information (PHI), payment information, or covered unclassified information (CUI). It is crucial to understand that how this data is sent or shared, stored and received is any organizations biggest threat.
Why is Secure Enterprise or Organizational File Sharing Important?
It is highly probable that you have all sent or received data, information and/or files/folders at some point or another. It is also highly likely it has occurred in or around a workplace or home office. It may be surprising that so many businesses don’t think that the way the share files and information is a security risk. “Cyber perils are the biggest concern for companies globally in 2022,” according to the Allianz Risk Barometer. Cyber incidents top the Allianz Risk Barometer for only the second time in the survey’s history (44% of responses).
Here are several additional facts from across the cybersecurity landscape that Forbes compiled in January 2022:
- Cybercriminals Can Penetrate 93% of Company Networks (betanews.com)
- “Among the findings of a new study of pentesting projects from Positive Technologies, conducted among financial organizations, fuel and energy organizations, government bodies, industrial businesses, IT companies and other sectors. In 93 percent of cases, an external attacker can breach an organization's network perimeter and gain access to local network resources.”
- Businesses Suffered 50% More Cyberattack Attempts per Week in 2021 (darkreading.com)
- The rise — partly due to Log4j — helped boost cyber attack attempts to an all-time high in Q4 2021, new data shows. The education/research sector sustained the most attacks in 2021, followed by government/military and communications.
- Corporate Cyber Attacks Up 50% Last Year
- 2021 saw 50% more cyber-attacks per week on corporate networks compared to 2020. While many large businesses suffered breaches, small and medium businesses were an easier target for hackers because of the lack of resources and security expertise.
- Most Targeted Sectors Worldwide by Hackers in 2021:
- Education/Research sector up by 75%
- Cyber attacks on Healthcare sector up by 71%
- ISP/MSP up by 67%
- Communications +51%
- Government/Military sector up by 47%
These attacks are evolving to be more complex, frequent, and targeted. Accenture’s Cost of Cybercrime Study found that almost half (43%) of cyber-attacks are aimed at small business but only 14% are prepared. Small to mid-sized organizations around the world have shared their recent cyber security experiences:
- Insufficient Security Measures: 45% say that their processes are ineffective at mitigating attacks.
- Frequency of Attacks: 66% have experienced a cyber-attack in the past 12 months.
- Background of Attacks: 69% say that cyber-attacks are becoming more targeted.
Security breaches disrupt normal organization operations, but it can also cause irreparable damage to IT infrastructure, assets, and brand equity if a business lacks the resources or finances repair the damage. It is imperative that your organization and IT team are staying up to date on the cybersecurity trends on common vulnerabilities, mitigation tactics, repercussions of an attack, and the state of cyber threats in general. It’s important to state there is no such thing as a perfect security solution, but your organization should have multiple ways of deterring bad actors like multiple walls around a castle keep.
Data Breaches You Should Know About (If You Don’t Already)
Have you ever thought about where all the data that hackers want exists? Almost all organizations have their data and information in files on servers. Guess what most attackers are interested in? They want one thing – a profit from their work. They want the files that have valuable data like financial information, personal health information (PHI), trade secrets or proprietary information, credentials, personally identifiable information (PII) and more. This data can sit in documents, files used in data transfers, databases, and more. Basically, this means that however you create these files (and share them) is the focus of a cyberattack.
Accellion
What Happened?
Accellion File Transfer Appliance (FTA) was a file sharing service that was compromised due to zero-day vulnerabilities in their service. This vulnerability allowed hackers to place a DEWMODE web shell on the victim’s servers. This allowed the bad actors to exfiltrate files on servers from enterprises operating Accellion’s appliance in their in-house infrastructure.
In mid-December Accellion was alerted by a customer of a zero-day vulnerability in the product. Accellion investigated this for three days and then released a patch. By February 2021 there had been four more vulnerabilities discovered and addressed.
Accellion’s clients were using their FTA to securely transfer files that were too large or too sensitive to send via email. Prior to these attacks Accellion was phasing out the FTA and even encouraged their clients to move to a new (at the time) file transfer tool – Kiteworks.
Just four months prior to the legacy file transfer solution being retired in April of 2021 – it was attacked by two advanced persistent threat (APT) groups that were connected to FIN11 and the CLOP ransomware gang. The hackers exploited the FTA vulnerabilities to access Accellion client files that they were able to exfiltrate. This impacted over 100 companies, universities, government agencies and organizations and millions of individuals globally. The long list of Accellion’s high-profile customers that have made statements regarding the security breach includes Bombardier, Kroger (family of companies/pharmacy), Royal Dutch Shell, University of California, Stanford University, the University of Colorado, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, Morgan Stanley, Singtel, Trinity Health, U.S. Dept. of Health, and Human Services and more.
The Consequences
The $8.1-million class action lawsuit accused Accellion of failing to implement and maintain the necessary security practices to protect customers’ sensitive information. Additionally, the are accused of failing to identify vulnerabilities in the security of the FTA. Plaintiffs also alleged that Accellion did not disclose the vulnerabilities or the inadequate security practices.
According to California federal court filings, Accellion claims no responsibility or liability for the data breach and denied all the allegations.
SolarWinds – Orion
What Happened?
SolarWinds is a software company that provides system management tools for infrastructure and network monitoring along with other technical services to organizations globally serving more than 30,000 public and private companies – this includes federal, state, and local government agencies. The product that was used for the attack is an IT performance monitoring system called Orion. This system had administrative access to IT systems that contains log and system performance data. The global use of this service made SolarWinds an attractive and lucrative target.
In mid-2019 the Threat actors gained unauthorized access to the SolarWinds network. By mid-2020 SolarWinds was being used as a springboard to compromise U.S. government agencies and was said to be “the largest and most sophisticated attack the world has ever seen,” by Microsoft Corp President Brad Smith. The extent of the attack is unprecedented and is likely the largest of its kind ever recorded.
“I think from a software engineering perspective, it’s probably fair to say that this is the largest and most sophisticated attack the world has ever seen,” Smith said during an interview that aired on Sunday on the CBS program “60 Minutes.”
Smith stated “When we analyzed everything that we saw at Microsoft, we asked ourselves how many engineers have probably worked on these attacks. And the answer we came to was, well, certainly more than 1,000.”
The attack gave hackers access to more than 18,000 thousand SolarWinds customers that managed their IT resources using the Orion network management system. This data breach occurred when SolarWinds accidentally opened a backdoor for malware as an update to the Orion software. The malicious “update” (Trojan Horse) allowed the malware to spread undetected and compromised the networks, systems, and data of SolarWinds customers and more. For example, the attackers were able to gain access to sensitive information like emails at the U.S. Treasury, Justice and Commerce departments and other agencies.
Unfortunately, the hack exposed the data of Orion users too. This means that the hackers could potentially gain access SolarWinds customer information technology system – i.e. the networks and data of their partners and customers. This could have allowed them to use those systems to install more malware and spy on other organizations.
The Consequences
The SolarWinds security breach will have long-term impacts but there are still unanswered questions. This attack is considered a cyber catastrophe. This has industry and government leaders rethinking how software is made and secured. This means more scrutiny for software companies used in the supply chain.
A company quarterly report shows that the SolarWinds Orion security breach cost the company $40 million dollars in the first nine month. This is a huge reputational and financial burden for the company to carry. Although, this is partially offset by insurance. In an SEC filing SolarWinds states “Although the ultimate magnitude and timing of expenses or other impacts to our business or reputation related to the cyber incident are uncertain, they could be significant.”
Eric Byres, CEO of aDolus, a software supply chain firm for Operational Technology (OT) stated that the Orion attack is “probably one of the two most significant attacks ever. And the other one was Stuxnet,” and “Both of them were intended for military, political, or intelligence purposes.”
The financial losses for SolarWinds and the victims of this attack are not the only consequences. This cybersecurity breach showed the U.S. government the rising sophistication of the cyber capabilities of our adversaries. In May 2021 the White House implemented a cybersecurity executive order that established improvements for the software supply chains. This included a requirement for a software bill of materials (SBOMs) for federal contractors. This means with the governments wide reaching procurement influence its likely to see a trickle-down effect for SBOMs across the tech industry.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends five cybersecurity functions: identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. There is a disconnect between security and IT allowing opportunities for hackers partly due to the reliance on only protection capabilities. It’s not just about keeping the bad guys out – there are four other pillars to the NIST framework. The framework is universal. The sole purpose is not for software makers alone. Organizations need to WHAT is running in the assets on their networks.
“And that’s what the world and America really lacked. And SBOMs really give us that ability to identify and detect and respond,” said Byres.
On their own, they’re useful — but SBOMs are only meant to be building blocks, according to Byres, who has worked on the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) and CISA committees for the SBOM movement.
The Orion compromise leaves the lingering issue that companies were not prepared to identify what was in their system. Theoretically, SBOMs could reduce the time it takes to find the corrupted code. At best the SBOMs will establish negligence standards. There is a demand for greater expectations during the build process because there will always be vulnerabilities in software.
SolarWinds – ServU FTP for Windows
What Happened?
As previously mentioned, SolarWinds is a software provider. In mid-July of 2021 SolarWinds released an emergency update to patch a zero-day security vulnerability in ServU FTP for Windows. This was actively exploited in the wild by a single bad actor. The Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) detected the zero-day remote code execution exploit being used to attack the SolarWinds Serv-U FTP software in limited and targeted attacks. This exploit was initially identified in a routine Microsoft 365 Defender scan. The software noticed an “anomalous malicious process” as described in detail in this Microsoft blog post. It seems the hackers were attempting to make themselves Serv-U administrators, among other suspicious activity.
The attackers originally gained access to a vulnerable server by taking advantage of an Orion API vulnerability (CVE-2020-10148). They got around the SSH authentication flaw and deployed a Supernova Webshell on the disk via a Powershell command. This opened the door for the hackers to take aim at all internet facing SSH servers and ports in the target industries and create a backdoor.
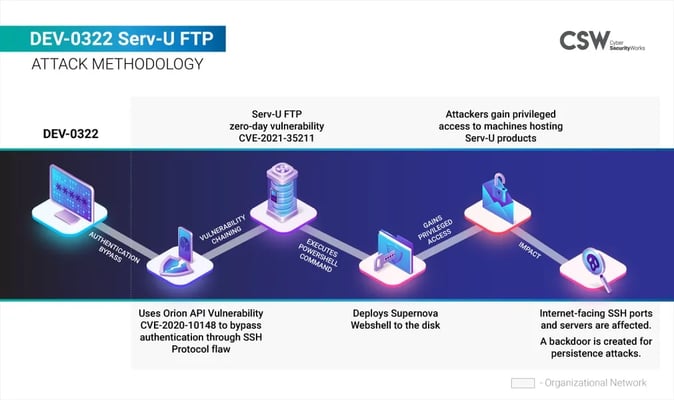
Security researcher Jonathan Bar Or discovered the flaw that affected Serv-U releases from May 5th 2021 and earlier. To address this the company released a hotfix and later patched the exploit in Serv-U version 15.3. Microsoft stated that the hackers targeted SolarWinds Serv-U servers by “connecting to the open SSH port and sending a malformed pre-auth connection request,” this enabled DEV-0322 operators to take over vulnerable devices by running malicious code on the targeted system. In layman’s terms this means that regardless of a local user’s permissions they could create a file defining a new Serv-U FTP admin account giving themselves full access to the C:\ drive. By doing so, the account could log in via FTP and replace or read any file available on the drive. So, if Serv-U’s Secure Shell (SSH) protocol connected to the internet, the hackers could “remotely run arbitrary code with privileges, allowing them to perform actions like install and run malicious payloads, or view and change data.” Serv-U announced that any customers running older Serv-U software should update as soon as possible.
The Consequences
Secure Shell (SSH) is a widely utilized protocol for secure communication over an untrusted network. One of the reasons the attacks were successful is due to some of the ServU binaries not being protected by Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR). ASLR randomizes the applications memory location preventing attackers from corruption an apps memory by targeting any specific memory sections. Since this protection was missing is made it simple to exploit the Serv-U zero-day.
“Enabling ASLR is a simple compile-time flag which is enabled by default and has been available since Windows Vista,” – Microsoft Engineers
ServU did note that there was no downstream impact because the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers ignored improper characters. Anyone using the ServU file transfer tool can avoid being attacked by either installing the hotfix or disabling SSH access to their servers.
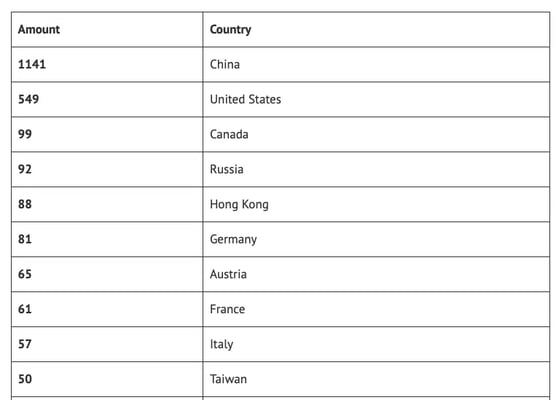
"In July, 5,945 (~94%) of all Serv-U (S)FTP services identified on port 22 were potentially vulnerable. In October, three months after SolarWinds released their patch, the number of potentially vulnerable servers [was] still significant at 2,784 (66.5%)," warned NCC Group researchers in their report.
Despite all the alerts sent out to apply the security update there are still vulnerable ServU servers that are publicly accessible. Most of these servers are in China with the United States coming in second. As of November 2021, the percentage of potentially vulnerable servers was still above 60%, 6 months after the incident occurred!
Preventing and Safeguarding Your Organization from a Data Breach
All businesses store and generate sensitive information. To the naked eye it may just look like design plans or employee tax information, but to a hacker its lucrative intellectual property and social security numbers. Unfortunately, this information is surprisingly easy to access if there is no digital security plan.
It has been said that a business is only as important as the content it owns. This can also be applied to how effectively you safeguard your clients’ business interests. If your business often handles proprietary data for your clients – engineers, defense contractors, lawyers, manufacturers, or IT management – it is your responsibility to ensure their information is safe. Your customers business may rely on your ability to protect their content, proprietary information, and in general – their data.
The following are some of the best ways to prevent file sharing data breaches:
- Employee Training and Education
- Regular Security Audits
- Work from Home Plan
- Strong Passwords
- Response Plan for Data Breaches
- Software and System Updates
- Data Use, Management, Storage, and Maintenance Plan
- Physical Security
- Asset Inventory
- Network and File Server Monitoring
Cybersecurity Threat Trends
- The continued impact of permanent remote work due to COVID-19 – More employees have moved to work-from-home jobs than ever before. Remote working has increased the amount of reliance organizations have on digital communication, file sharing/file transfer, video conferences, collaboration tools, and more. Why wouldn’t cyber criminals continue to exploit a lack of cybersecurity awareness at home where employees feel the safest?
- A continuing incline in malware cyber security threats - with ransomware being a particularly expected form of them. The frequency of ransomware attacks has increased from one every 40 seconds in 2016 to one every 11 seconds in 2021 and they are growing more sophisticated. In 2022 it is expected there will be an increase in malware hidden inside seemingly legitimate software updates. This will of course allow hackers to exfiltrate and spread malware to a wide range of victims.
- Increase in attacks via the Internet of Things (IoT) – connected electronic devices. While attacks via the IoT are already evident, 2022 will most probably see a rise in not only individual threats but also the further sophistication of their delivery methods.
- Cyber criminals will move from identity theft to identity fraud - Criminal are accumulating personal identifying information, but they’re not using it to target consumers as much as they used to do. Rather, they’re using it in credential attacks on businesses. The increase in fraud will lead to another development in 2022, a behavior change as consumers withdrawing from certain kinds of online activity.
- A rise in preventive measures, to better counter cyber attacks - 2022 is the year that we’ll continue seeing a rise in AI-based cybersecurity, with the technology becoming more and more sophisticated as machine learning develops to prevent all sorts of conducted attacks.
It is important to note that organizations that acknowledge these threats and implement the necessary technology, services, and training are much more likely to stay safe.
- It took an average of 287 days to identify a data breach (IBM).
- The average time to contain a breach was 80 days (IBM).
- Healthcare and financial industries had the longest data breach lifecycle — 329 days and 233 days, respectively (IBM).
- The data breach lifecycle of a malicious or criminal attack in 2020 took an average of 315 days (IBM).
- Microsoft Office files accounted for 48 percent of malicious email attachments (Symantec).
- From 2016 to 2018, the most active attack groups targeted an average of 55 organizations (Symantec).
Conclusion
The digital landscape is constantly changing. This means it is crucial to keep up with the impact of cyber trends. Cyberattacks are evolving from how they impact a business, the method(s) of attack, and what they target. The Ninth Annual Cost of Cybercrime Study conducted by Ponemon Institute and jointly developed by Accenture identified that cyberattacks are changing due to the following:
- Evolving Targets: The target with the fastest growing consequences and most costly repercussions is – information theft. Industrial controls and other core systems or OT (Operational Technology), are being attacked in a dangerous trend to disrupt and destroy.
- Evolving Impact: Even though data remains a target, data theft is not always the outcome. A new trend in cyberattacks is not only copying data – but destroying it – or even changing it in an attempt to breed distrust. The attack on data integrity – or preventing data toxicity – is the next frontier.
- Evolving Techniques: Hackers aka cyber criminals are adapting their methods of attack. They are focusing in on the weakest link in cyber defense – the human element – through increased social engineering, phishing and ransomware attacks as a path to entry. Recently there has been a rise in nation-states and their associated attack groups attacking commercial organizations using these social engineering techniques. Cybersecurity insurance claims are on the rise and attempts are being made to categorize attacks from these sources as ‘acts of war’ to limit settlements.
Some organizations may need simple file storage and sharing with limited security. Others will need a more advanced solution for their sensitive files and data, which means they will need a security-focused provider like Sharetru.
Sharetru serves as more than just a file-sharing and file transfer service for our clients. We act as a strategic partner that offers a range of storage and sharing solutions, plus compliance with many of the commonly used cybersecurity standards and frameworks.
In closing, it is more important than ever to ensure your business is protected in all aspects of cybersecurity, but particularly the safe transfer of files. Additionally, thoroughly training all users is the easiest way to safeguard against the risks associated with file sharing. If you haven’t already, you should consider investing in a cloud-based, business focused, secure system like Sharetru’s FTP Cloud and GOVFTP cloud. Interested in seeing it in action? Contact us today for a brief demo and a chance to ask questions about secure file sharing and storage for your organization.





